How To Deal With The Serial Number Of The Data Packet In BLE
What is the data packet confirmation process?
The data packet confirmation and flow control mechanisms of the Bluetooth low energy link layer are applied to all ACL connections and connection isochronous flows (CIS). PDUs refer to data physical channel PDUs or connection isochronous stream data PDUs.
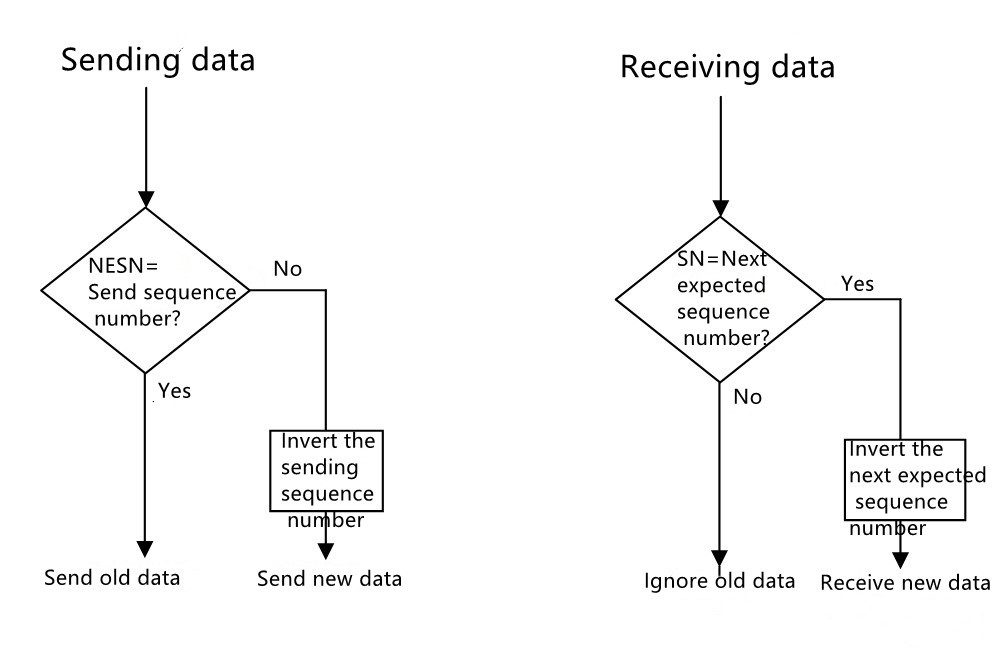
The link layer has two parameters in each Bluetooth low energy connection: send sequence number (SN) and next expected sequence number (NESN), each parameter represented by a bit. The sending sequence number is used to distinguish the data packets sent by the link layer; the next expected sequence number is used by the link layer to confirm the data packet sent last time by the connected device or request to resend it.
The Send Sequence Number and Next Expected Sequence Number parameters should both be set to 0 when an ACL connection or Connection Isochronous Stream (CIS) is just created.
If the last transmitted Data Physical Channel PDU used LE Coded PHY, the coding scheme used for retransmission may not be the same as the coding scheme used for the previous transmission. If a PHY update procedure occurs while waiting for a data physical channel PDU to be retransmitted, it will be retransmitted with the new PHY.
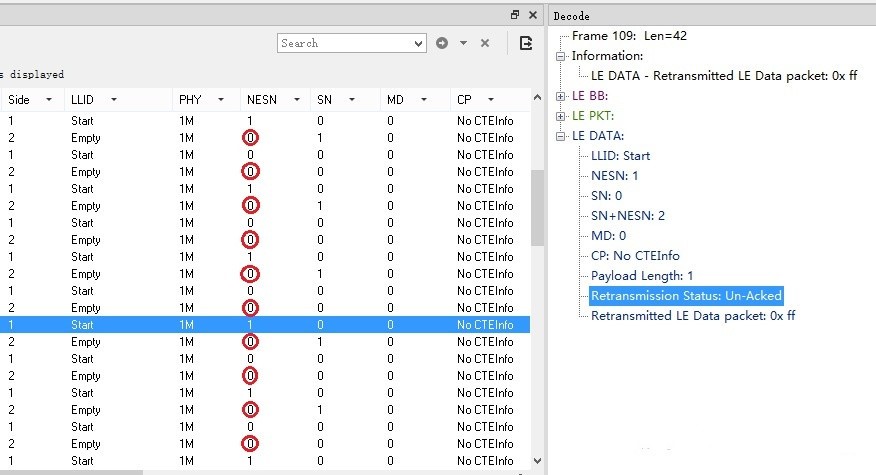
The new PDU refers to the PDU initially sent by the link layer; the previous PDU refers to the PDU retransmitted by the link layer. When resending the data physical channel PDU, the other parts of the data packet except the NESN bits in the header should be the same as the data physical channel PDU sent by the link layer last time.
For each new PDU, the SN bits in the header shall be set to the [sending device's] transmit sequence number bit value; for each transmitted PDU, the NESN bits in the header shall be set to the [sending device's] next desired sequence number bit value.
The value of the SN bits in the PDU shall be compared with the value of the Next Expected Sequence Number (NESN) bits of the [receiving device] after each PDU is received. If the comparison result shows that the two are different, it indicates that this PDU is a PDU that is sent repeatedly, and the value of the next expected sequence number bit should be kept unchanged and the data packet should be ignored; Invert the next expected sequence number bit value and receive this packet.
The value of the NESN bits in the PDU shall be compared with the value of the Transmit Sequence Number (SN) bits [of the receiving device] after each PDU is received. If the comparison result shows that the two are the same, it means that the PDU sent last time has not been confirmed and should be resent immediately; if the comparison result shows that the two are different, it means that the PDU sent last time has been confirmed, and a new PDU can be sent.
If the CRC in the received PDU is invalid, the value of the next expected sequence number bit shall remain unchanged to indicate that the PDU is not acknowledged as received. Since the received PDU has been rejected, the next expected sequence number bit value from the peer device cannot be trusted, so the last PDU sent from this device was not acknowledged and must be resent with the send sequence number unchanged.
SN and NESN bit values in a PDU qualified by the CRC check shall be used; when the SN bit value of the received PDU is the same as the SN bit value in the last received PDU, the payload of this PDU shall be ignored.
What is the flow control mechanism?
When the link layer of the local device cannot correctly receive the data packet sent by the connected device for any reason, it will not update the next expected sequence number (NESN) bit value, which will cause the connected device to resend the data packet, which is activated flow control.
Following as Packet Ack and Flow Control Example:
An example of successfully receiving a data packet and cyclically updating the NESN bit value between "1" and "0" is shown in the figure below, correspondingly, the SN bit value is also cyclically updated between "1" and "0".
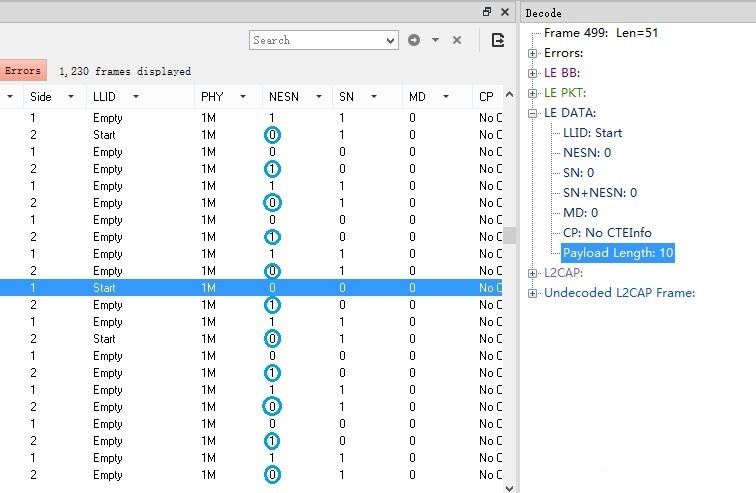
An example of an unsuccessful reception of a packet causing the NESN bit value to remain unchanged and triggering a retransmission is shown in the figure below.