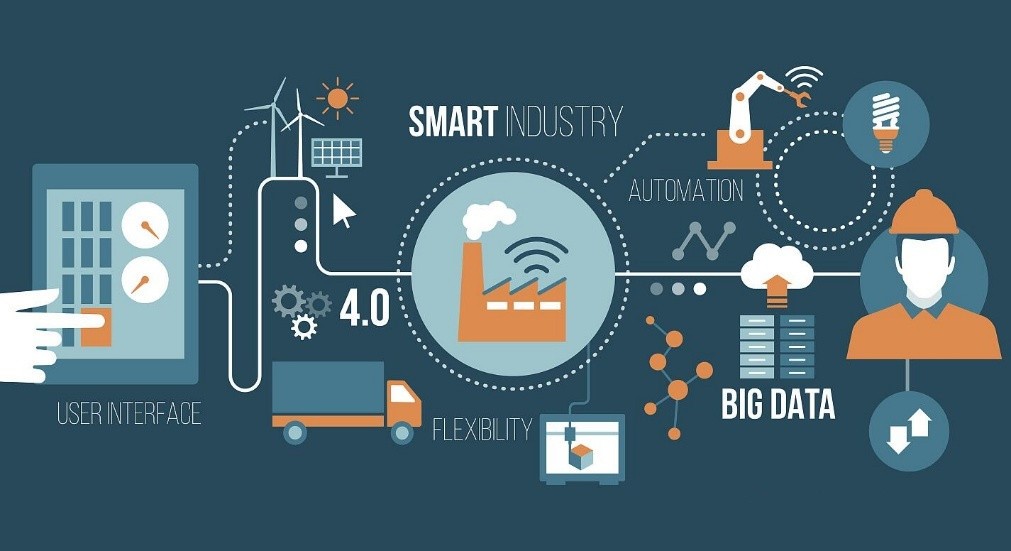
What is IIOT?
IIoT is the abbreviation of Industrial Internet of Things. It integrates various acquisition and control sensors or controllers with sensing and monitoring capabilities, as well as mobile communication, intelligent analysis and other technologies into all aspects of the industrial production process. Significantly improve manufacturing efficiency, improve product quality, reduce product cost and resource consumption, and ultimately realize the promotion of traditional industries to a new stage of intelligence.
According to relevant data, by 2025, the number of connections with the global Industrial Internet of Things will reach 13.8 billion, of which the number of connections in Greater China will reach 4.1 billion, accounting for about 1/3 of the global market. At the same time, according to a survey by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the annual revenue growth rate of China's industrial IoT market is about 25%, and it will exceed 500 billion yuan in 2022. This indicates that the IIoT is ushering in a period of rapid development.
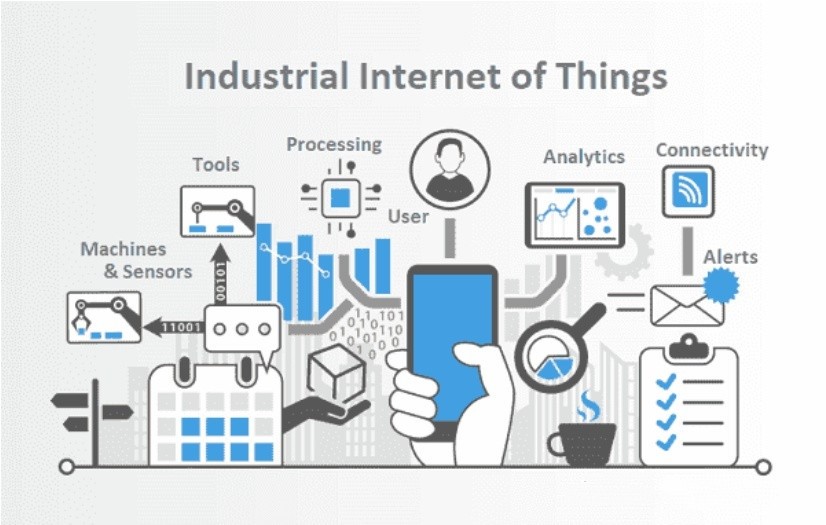
With the Industrial Internet of Things, businesses can make more informed optimization decisions thanks to real-time perception monitoring during operations. These connections can also increase efficiency by establishing remote access. Devices with sensors for the IIoT can communicate with each other, making automated systems more flexible. IIoT devices can also reduce energy consumption by adjusting to use only relevant functions.
What are the advantages of IIoT?
1. Production System Awareness and Monitoring
At the heart of an IIoT solution is continuous communication between systems and machines to ensure optimized throughput and real-time identification of machine defects
2. Manufacturing process optimization
Machines and equipment equipped with sensors and managed using IIoT systems can monitor conditions, equipment and workflows such as machine performance, assembly line management, supply chain optimization, workforce safety or quality assurance processes for optimization.
3. Predictive maintenance
Over 75% of equipment and system failures occur without notice. With IIoT, preventive maintenance combines analytics to predict machine failure.
4. Optimize quality
It instantly resolves issues on the production line, reducing downtime, lost productivity and product defects, and IIoT devices are programmed to monitor material quality, analyze equipment performance in real-time, and measure and measure finished products.
5. Inventory and Supply Chain Management
Data, analytics, insights and contextual intelligence enable inventory systems to operate seamlessly to more accurately estimate available material, work in process and ETA for new materials, which can help optimize supply chains and cut costs.
6. Customer Service Levels and Satisfaction
Sensor-equipped production systems and inventories can enable customers to see the progress of their orders in near real-time. Sensors provide insights into customer usage that can help manufacturers improve functionality, alert customers to issues and bottlenecks, and differentiate themselves from the competition.
7. Worker Safety and Health
Smart wearables allow managers to monitor the health and safety of production workers by tracking the history of illnesses and injuries, absences, mistakes, machinery or vehicle accidents, or life-threatening events such as gas leaks.
8. Energy Management and Sustainability
Industrial manufacturing consumes 54% of the world's electricity. Manufacturers using the IIoT can significantly improve energy efficiency by optimizing energy consumption.
9. Service provisioning and coordination
Industrial IoT-enabled field service delivery is a value-based approach based on factors provided, such as the timing of a given service activity, context, and technician involvement.
10. Service Contract Compliance and Performance
IIoT enables real-time data visibility, so both original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and users can be aware of risks and problems as they arise.
What are the challenges of IIoT?
1. lack of standardization
There are many different formats and technologies that meet the different requirements of machine-to-machine communication between connected devices, such as Sigfox and Zigee technologies, which must be interoperable for an IIoT environment.
2. Compatibility with legacy equipment technologies
Many older devices are not designed to provide the relevant specific format for modern technology, so factory equipment from decades old may require some retrofit to communicate with complex IIoT devices.
3. Safety
Any device is controlled by network communication, which is easy to be hacked in the face of the Internet, IIoT has no way to avoid this, and many low-cost devices such as remote cameras, routers and even DVRs have limited security features (including hard-coded default passwords and telnet access), or never update the patch. Once compromised, they can cause problems such as DDos attacks and malware distribution.
As the IIoT spreads, these technologies will become more accessible and affordable, and the benefits can offset the initial cost. Tighter cybersecurity standards can address growing cyber threats. While the IIoT is still relatively new and faces some challenges, the technology can give those who successfully implement it a competitive advantage.